Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronou Counter 36+ Images Result
Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronou Counter. Draw the logic diagram based on the equations obtained. The counter enumerates (i.e., goes through) the following sequence:
Initially, all flip flops store zero, hence, the complemented output will be 1. Output of ff0 drives ff1 which then drives the ff2 flip flop. A timing diagram is shown below.
3d electrical switch wiring diagram harley starter relay wiring diagram 1993 saturn wiring diagram wiring diagram linhai scooter
Proposed QCAbased 3bit synchronous counter. (1) block
All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. Output of ff0 drives ff1 which then drives the ff2 flip flop. All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. In the up counter the 4 bit binary sequence starts from 0000 and increments up to 1111, i.e from 0 to 15.
![[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL [DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL](https://i2.wp.com/image3.slideserve.com/6160351/a-3-bit-synchronous-binary-counter-n.jpg)
Source: ediagramming.visualacademy.it
As it is a two bit down counter , so we require 2 flip flops: Timing diagram for 3 bit up counter. Types 4 bit synchronous up counter: Draw timing diagram with 8 clock pulses. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram.

Source: tutorialspoint.dev
As it is a two bit down counter , so we require 2 flip flops: All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. Output of ff0 drives ff1 which then drives the ff2 flip flop. When the first clock pulse arrives, the.

Source: youtube.com
The jb and kb inputs are connected to qa. Its operating frequency is much higher than the. In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. The output of tff1 is fed as an input for tff2. Synchronous counter design using novel level sensitive t.

Source: eduladder.com
Initially, all flip flops store zero, hence, the complemented output will be 1. A timing diagram is shown below. X=0 and x =1 indicates that the counter counts up when input x = 0 and it counts down Timing diagram for 3 bit up counter. The counter enumerates (i.e., goes through) the following sequence:

Source: youtube.com
Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. The jb and kb inputs are connected to qa. The flipflop we are going to use is jk flip flop. In the up counter the 4 bit binary sequence starts from 0000 and increments up to 1111, i.e from 0 to 15. Initially, all flip flops store zero, hence, the complemented.
Source: multisim.com
Notice that the counter progress through a binary count of 0 through 7 and the recycle to the 0 states. Its operating frequency is much higher than the. In asynchronous counter, a clock pulse drives ff0. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. As it is a two bit down counter , so we require 2 flip flops:

Source: geeksforgeeks.org
Initially, all flip flops store zero, hence, the complemented output will be 1. Answer this question 10 mark question | asked in digital logic 2072 suggest us All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. Draw the logic diagram based on the equations obtained. Notice that an arrangement different from that for the asynchronous counter must be used.

Source: researchgate.net
In asynchronous counter, a clock pulse drives ff0. Notice that the counter progress through a binary count of 0 through 7 and the recycle to the 0 states. Synchronous counter design using novel level sensitive t. Output of ff0 drives ff1 which then drives the ff2 flip flop. The counter enumerates (i.e., goes through) the following sequence:

Source: youtube.com
After completing this tutorial, you should be able to. In asynchronous counter, a clock pulse drives ff0. Output of ff0 drives ff1 which then drives the ff2 flip flop. Its operating frequency is much higher than the. The output of tff1 is fed as an input for tff2.

Source: vdocuments.mx
In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. Initially, all flip flops store zero, hence, the complemented output will be 1. For a ripple up counter, the q output of preceding ff is connected to the clock input of the next one. Types.

Source: picturenewidea.blogspot.com
Timing diagram for 3 bit up counter. When the first clock pulse arrives, the negative edge triggers flip flop a and the output goes from 0 to 1. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. Draw the logic diagram based on the equations obtained.
![[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL [DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL](https://i2.wp.com/d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2F54c%2F54c88969-4847-4f60-be31-248f804407e6%2FphpNNo15O.png)
Source: ediagramming.visualacademy.it
Its operating frequency is much higher than the. The flipflop we are going to use is jk flip flop. Notice that an arrangement different from that for the asynchronous counter must be used for the j1 and k1 inputs of ff1 in order to achieve a binary sequence. As it is a two bit down counter , so we require.
![[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL [DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/13/81/9e/13819e1930ff400a0ce4bd6f381f8b51.png)
Source: ediagramming.visualacademy.it
For a ripple up counter, the q output of preceding ff is connected to the clock input of the next one. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. The output of tff1 is fed as an input for tff2. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. Answer this question 10 mark question | asked in digital.

Source: youtube.com
For a ripple up counter, the q output of preceding ff is connected to the clock input of the next one. All j and k inputs are connected to logic 1. Timing diagram for 3 bit up counter. After completing this tutorial, you should be able to. The output of tff1 is fed as an input for tff2.

Source: researchgate.net
The jb and kb inputs are connected to qa. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. Notice that the counter progress through a binary count of 0 through 7 and the recycle to the 0 states. Draw the logic diagram based on the equations obtained. For a ripple up counter, the q output of preceding ff is connected.

Source: cssimplified.com
Notice that the counter progress through a binary count of 0 through 7 and the recycle to the 0 states. When the first clock pulse arrives, the negative edge triggers flip flop a and the output goes from 0 to 1. In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. In the up.
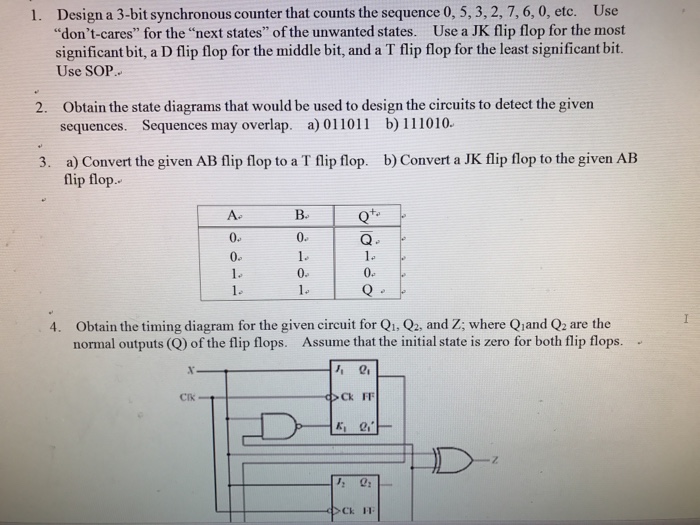
Source: chegg.com
After completing this tutorial, you should be able to. The flipflop we are going to use is jk flip flop. Show the binary counting sequence on the timing diagram. In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. The jb and kb inputs are connected to qa.

Source: youtube.com
The output of tff1 is fed as an input for tff2. In asynchronous counter, a clock pulse drives ff0. Draw timing diagram with 8 clock pulses. The flipflop we are going to use is jk flip flop. The jb and kb inputs are connected to qa.
![[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL [DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL](https://i2.wp.com/d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2Fdea%2Fdea0f11a-260d-496a-a684-23d3b7bec4f4%2FphplpsQZr.png)
Source: modulatordiagram.magnetikitalia.it
The flipflop we are going to use is jk flip flop. The counter enumerates (i.e., goes through) the following sequence: Notice that the counter progress through a binary count of 0 through 7 and the recycle to the 0 states. In the above image, the basic synchronous counter design is shown which is synchronous up counter. Show the binary counting.
![[DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL [DIAGRAM] Logic Diagram Of 3 Bit Synchronous Counter FULL](https://i2.wp.com/image1.slideserve.com/3085365/four-bit-asynchronous-binary-counter-and-its-timing-diagram-l.jpg)
Source: ediagramming.visualacademy.it
In the up counter the 4 bit binary sequence starts from 0000 and increments up to 1111, i.e from 0 to 15. In asynchronous counter, a clock pulse drives ff0. Its operating frequency is much higher than the. The complimented output goes from 1. For a ripple up counter, the q output of preceding ff is connected to the clock.